Substrate concentration, enzyme concentration, temperature and pH affect the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction.
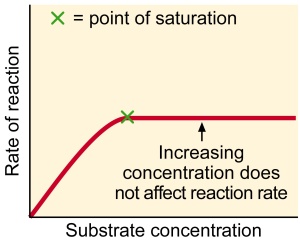
Substrate concentration- the rate of reaction increases with substrate concentration until a maximal velocity (Vmax) is reached. At low substrate concentration the active sites of the enzymes molecules are not used up. There are not enough substrate molecules to occupy all the active sites. As the substrate concentration increases more and more active sites come into use until all are being used (saturation) .any further increase in substrate concentration cannot increase the rate of the reaction.
Enzyme concentration- the active site of an enzyme maybe used over and over. Enzymes work efficiently at low concentrations. The rate of enzyme reaction is proportional to the enzyme concentration once substrate concentration is high and pH and temperature are kept constant.
Temperature- the reaction velocity is increased until a peak velocity is reached. This is due to an increased number of molecules having the activation energy to pass over the energy barrier. Also there is an increase in collision frequency of the molecules. There is a decrease of velocity with higher temperature because the high temperature results in denaturation of the enzyme. 35 ⁰C – 40⁰C is the optimum temperature required for human enzymes.
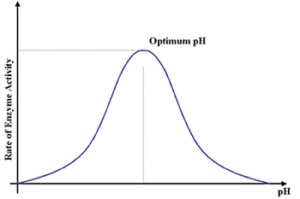
pH-enzymes have a optimum pH range at which they work best and they function within a narrow pH range. The optimum pH is that where the maximum rate of reaction is achieved. When pH is altered above or below this value the rate of enzyme reactivity decreases. As ph decreases the acidity increases. Therefore increasing the number of positive charge. Changes in pH alter the ionic charge of the acidic and basic side groups. This disrupts the bonding that maintains the specific shape of the enzyme. Therefore leading to a change in shape of the enzyme and active site. Extremes in pH cause the enzyme to be denatured.
References: http://youtu.be/FPKAJlgMCbE