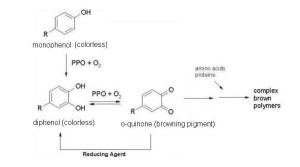
Enzymatic browning ia a chemical process which occurs in fruits and begetables by the enzymes phenolase, peroxidase and other enzymes that create melanine and benzoquione from natural phenols resulting in a brown colour. The enzymes are both oxidoreductases which transfer electrons or hydride ions from one molecule to another. Phenolase catalyses monophenols to diphenols, diphenols ca be further catalysed to produce quione. Catecholase and monophenolase are two types of phenolases. Peroxidase is responsible for the oxidation of H₂O₂ which is its optimal substrate.
Enzymatic browning can be prevented by:
- Lowering the pH and the copper cofactor necessary for the enzyme to function.
- Blanching to denature enzymes.
- Low temperatures reduce the rate of reaction
- Addition of chemicals such as citrates
- Addition of nitrogen gas to prevent the oxygen from reacting
References: http://www.en.wikepedia.org/wiki/Browning_(food_process)